Many species of cichlid fish, or fish in the Cichlidae family, go by the name tilapia. These fish are only found in the Middle East and Africa. They are now farm-raised in over 80 countries worldwide. Tilapia is a popular food source due to its low cost and mild taste. Â.
Tilapia is known for its sweet, mild taste and flaky texture. But the taste can be very different depending on what the fish eat and how clean the water is where they live.
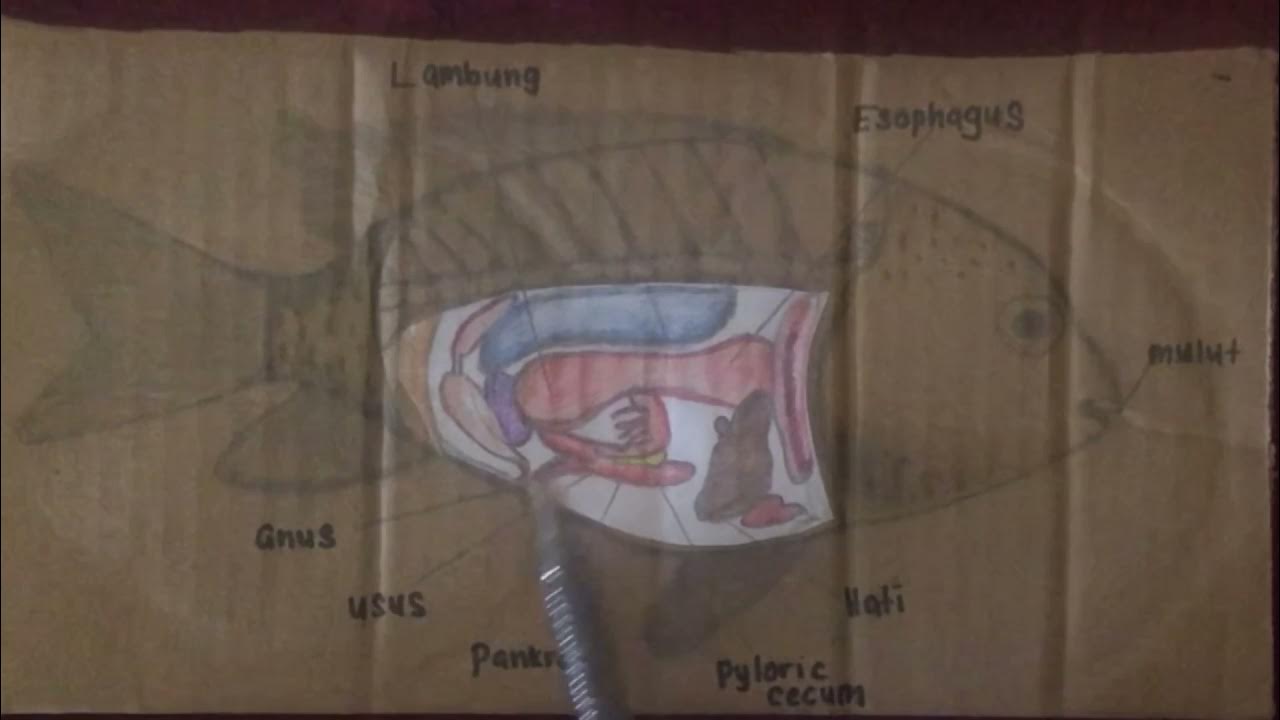
Tilapia are shaped like sunfish or crappie, with bodies that look fairly flat from side to side. They have long, spined fins. Color can vary by species.
In the wild, tilapia are found in fresh water, in rivers and lakes. Also, the fish have been accidentally brought into some brackish waters, which are places where salt water and fresh water meet.
Tilapia is a lean source of protein and provides some omega-3 fatty acids. (Photo Credit: Stockcreations/Dreamstime)
It also gives you vitamins and minerals like choline, niacin, vitamin B12, vitamin D, selenium, and phosphorus. And its a good source of healthy fats.
A mineral called selenium can help keep you from getting cancer, heart disease, memory loss, and thyroid disease. Although you only need a small amount of selenium, it is essential for various bodily functions. One fillet of tilapia has 188% of your daily value of selenium, making it a great source of this mineral.
Many of the health benefits of eating fish are due to their high omega-3 fatty acid content. These unsaturated fats benefit heart health by:
Omega-3s help keep the membranes around all of your cells healthy. They are also very important for your lungs and immune system, which fights off germs.
Its true that tilapia doesnt have as many omega-3 fatty acids as oily fish, like salmon and trout. But it has more than protein choices such as beef, pork, chicken, or turkey.
Tilapia is also high in omega-6 fats, from the vegetarian diet it eats. Another important fatty acid that your body can’t make itself is omega-6s, which you can mostly get from vegetable oils. These fats, in healthy amounts, can help keep your cholesterol and blood sugar under control. But most Americans eat more omega-6 fats and fewer omega-3 fats than is ideal for overall health.
Also, cooking fish in oil makes it less heart-healthy and raises the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Tilapia has many of the nutrients your body uses to make and maintain bones, such as:
Tilapia is a lean source of protein, so it can be part of a plan to lose weight, just like other fish. Fish can help you feel full without a lot of calories. In some studies, eating fish has been linked to weight loss. Â.
Vitamin B12 is found in large amounts in tilapia. It helps your body make DNA, keep your nervous system healthy, and make red blood cells. Its also low in fat, saturated fat, calories, carbohydrates, and sodium.
Tilapias nearly 23 grams of protein per serving fills you up and helps you feel full longer.
Tilapia are farmed fish that usually live in closed-off tanks, so they don’t come into contact with pollution as much as wild fish do. They also dont eat smaller fish, which can lead to a buildup of contaminants in big fish. This means they are lower in mercury than many other fish.
People who are pregnant or breastfeeding are encouraged to eat 8-12 ounces of low-mercury seafood each week. The recommended serving size for kids ages 1 to 3 is 1 ounce, and the recommended serving size for kids ages 4 to 11 is 4 ounces. Â.
Tilapia is a popular and affordable fish choice that provides lean protein, vitamin B12, selenium, and other beneficial nutrients But like any food, the speed of digestion can vary. So how long does it actually take for your body to digest tilapia?
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the tilapia digestion timeline and what factors impact how quickly your body can process this mild white fish.
Overview of Tilapia’s Nutritional Profile
Tilapia is low in fat and calories but high in protein. A 3.5 ounce (100 gram) serving contains:
- 128 calories
- 26 grams protein
- 3 grams fat
- 24% DV niacin
- 31% DV vitamin B12
- 20% DV phosphorus
It’s also rich in selenium, potassium, vitamin B6 and magnesium. This nutrient profile makes tilapia a heart-healthy protein source.
The Digestion Process for Tilapia
On average, digesting a meal takes 24-72 hours from start to finish. Fish like tilapia tend to be on the faster end, compared to red meats which take longer.
Here’s a closer look at the tilapia digestion timeline:
-
Mouth: Chewing begins mechanical digestion. Enzymes in saliva start breaking down carbohydrates.
-
Stomach: Tilapia is mixed with stomach acid and enzymes to further break down proteins. Takes ~1-2 hours.
-
Small Intestine: Bile and pancreatic enzymes continue breaking tilapia down into amino acids and fats into fatty acids. Takes ~2-6 hours.
-
Bloodstream: Nutrients from digested tilapia are absorbed through intestinal walls and enter bloodstream.
-
Colon: Remaining undigested material passes to colon. Water is reabsorbed, waste is eliminated 24-72 hours after eating.
So the entire process from swallowing tilapia to excretion takes about 1-3 days. Absorption of nutrients happens earlier in the small intestine within a few hours after eating.
Factors That Affect Tilapia Digestion Time
While tilapia takes 1-3 days to fully digest on average, several factors impact the digestion rate:
-
Cooking Method: Frying adds fat and slows digestion. Broiling, grilling or poaching are faster.
-
Portion Size: Bigger portions take longer. Stick to 3-4 oz serving sizes.
-
Individual Differences: Age, gender, metabolism and genetics affect digestion speed.
-
Food Combinations: Pairing with vegetables aids digestion. Refined carbs can slow it.
-
Gut Health: Digestive issues like IBS slow things down. Probiotics may speed it up.
-
Supplements: Digestive enzymes may help break down proteins and fats faster.
So the healthiest individuals eating broiled tilapia with vegetables may digest it on the faster side, within 24-36 hours. Those with impaired digestion may take closer to 72 hours to fully process the same meal.
Tips to Improve Tilapia Digestion
Here are some tips to help optimize digestion when eating tilapia:
-
Choose wild-caught or sustainably farmed tilapia when possible.
-
Avoid heavy breading or frying which can burden digestion.
-
Drink fluids during meals to aid digestion.
-
Chew thoroughly to increase surface area for enzyme action.
-
Take probiotics to support healthy gut flora.
-
Add lemon, herbs and spices to boost flavor without heavy sauces.
-
Allow 3-4 hours between eating tilapia and bedtime.
-
Exercise after eating to stimulate digestion.
-
Consider digestive enzymes or betaine HCl to boost protein breakdown.
Making small tweaks to how tilapia is prepared and eaten can ensure your body digests it as efficiently as possible within the typical 24-72 hour timeline.
Health Benefits of Tilapia
Despite being lean and quick to digest, tilapia offers many noteworthy health benefits:
-
High quality complete protein helps build and repair muscles.
-
Vitamin B12 is crucial for nerve function and energy metabolism.
-
Selenium boosts thyroid health and antioxidant activity.
-
Potassium aids blood pressure regulation.
-
Phosphorus supports bone mineralization.
-
Low in mercury and sustainably farmed.
Tilapia provides a nutritious protein source as part of a balanced diet. For most people, the benefits outweigh any minor risks.
Is Eating Tilapia Healthy?
While no food is perfect, tilapia offers more benefits than drawbacks:
Pros:
-
Rich in protein, B vitamins, selenium
-
Low in fat, carbs, calories
-
Quickly digested
-
Affordable and sustainable
Cons:
-
Has less omega-3s than fatty fish
-
Concerns over some farming practices
As long as you choose responsibly farmed tilapia and eat a varied diet, tilapia can be part of an overall nutritious way of eating. Any related digestion issues can often be managed with cooking methods, portion sizes and supplements.
On average, digesting tilapia takes 24-72 hours. However, factors like cooking method, portion size, and gut health impact how quickly you digest this mild white fish. Eating wild-caught or sustainably farmed tilapia broiled or grilled in sensible portions provides excellent nutrition and protein with minimal risks. With a few tweaks, most people can enjoy tilapia as part of a varied, healthy diet.
Potential Health Risks of Eating Tilapia Fish
Although eating tilapia offers many potential health benefits, it also carries some risk.Â
Eating large amounts of tilapia and other fish could expose you to certain cancer-causing chemicals. This is especially true in places where a lot of fisheries are close to industrial parks that pollute the water with heavy metals.
Tilapia allergy
An estimated 1% of people are allergic to some types of finned fish. New fish allergies can develop in adults. The most common problems are with salmon, tuna, and halibut, but tilapia can cause allergic reactions as well. If you’re allergic to one type of finned fish, you might also be allergic to others. If you’ve ever had a reaction to fish, like hives, stomach cramps, or trouble breathing, you should talk to your doctor about what’s safe for you. Â.
Tilapia farming
Many concerns about tilapia safety center on farming practices. But these practices are very different. The most worrying ones are those that involve fish farms in China, where a lot of the frozen tilapia in the US comes from. Â.
Some reports from the U. S. Chinese fisheries have been found to use a lot of antibiotics and feed fish animal waste, which could make the fish sick. Both the government and private seafood monitoring groups have found these practices to be questionable. Its unclear how widespread those practices are. Most farmed tilapia eat corn and soybean meal. Â.
Early in their lives, farm-raised tilapia may also be given hormones, but the hormones don’t stay in the fish that is caught. Such hormones are rarely used in North Americans farms.
The FDA has turned away some shipments of tilapia and other fish from China, but lets U.S. stores sell fish that was brought in from other countries. S. consumers must meet the same safety standards as food produced in the U. S.
Is tilapia high in cholesterol?
Tilapia has some cholesterol, about 55 milligrams in a 4-ounce serving. In comparison, an egg has about 200 milligrams of cholesterol and a small pork chop has about 85 milligrams. This doesn’t make it a high-cholesterol food, though. Tilapia has about the same amount of cholesterol as other fish, but less than shrimp and lobster.
Is tilapia a fake fish?
Tilapia are real fish. Humans have been catching tilapia in the wild for thousands of years. Farm raised fish are newer additions that were bred to make food production more efficient. They are real, though, and have skin and bones just like other fish. Â.
Is tilapia a junk fish?
Concerns about how tilapia is farmed and the fact that it has few omega-3 fats and many omega-6 fats have hurt its reputation. But it wouldnt qualify as a junk food under most standards â because it does have nutritional value. Â.
Tips to Source Safe Tilapia
Some people might not want to buy tilapia from China because they are worried about safety and the damage that the farms do to the environment because they are not well regulated. Roughly three-quarters of frozen tilapia sold in the United States come from China. Â.
To choose potentially safer tilapia with a lighter environmental impact, carefully read labels and consider:
- Buying tilapia from Colombia, Mexico, Indonesia, or Taiwan
- Asking restaurants the source of their tilapia
- Buying tilapia that is Aquaculture Stewardship Council, BAP Certified, or Naturland certified is a good idea.
- Buying locally raised tilapia from a farmers market, where available
Is farmed tilapia healthy?
Almost all tilapia on the market is farmed, and the FDA says fish sold in the U. S. is safe. If you are worried about how fish are raised in China or other places, it is best to buy fish that was raised in other countries or, if possible, from local farmers. Also, farming practices can change over time, so check for the most current information from watchdog groups.
Tilapia price
One reason tilapia is so popular is that its generally less expensive than other fish. Thats because tilapia are easy to farm, eat a low-cost plant diet, and are widely available worldwide.
5 of The Healthiest Fish to Eat and 5 to Avoid
FAQ
Is tilapia easy to digest?
How long does fish take to digest?
Why do bodybuilders eat tilapia?
How many times a week should you eat tilapia?
How long does food digestion take?
Overall, from when you swallow food it leaves your body as waste material. This process takes about 3 to 5 days, depending on the individual. At the same time, the entire digestive process is similar for everybody. The only difference is the time, Which you can calculate from the Food digestion time chart that is below.
How long does tilapia take to flush out dioxin?
Dioxin, also found in tilapia, is associated with increased cancer risks and other health issues. It’s pretty shocking how long it takes for the body to flush out this chemical–seven to eleven years. Saxitoxins are potent neurotoxins that can cause the condition called paralytic shellfish poisoning.
How long does it take for food to pass through the gut?
A look at the time it takes for food to pass through the gut from mouth to anus. In a healthy adult, transit time is about 24–72 hours. Read the article The human digestive system for further information. Digestive activity begins with the sights, sounds and smells of food.
Do Chinese tilapia eat animal feces?
According to various, Chinese farm-bred tilapia eat animal feces in their feed; mainly the fecal materials of duck, chicken, and pigs. Consuming such fish augments the chance of developing cancer ten times more than the wild fish. There’s reason to believe that these are not mere speculations.
