Tuna is a popular type of fish that is commonly eaten canned, fresh, or frozen. But if you’re following a low-oxalate diet, you may be wondering if tuna is a good choice or not In this article, I’ll take a detailed look at the oxalate content of different types of tuna to help you decide if it can fit into a low-oxalate meal plan
What are Oxalates?
Oxalates are compounds found naturally in many plant foods like leafy greens, beans, nuts, fruits, and grains. For most people, oxalates are harmless at normal intake levels However, for those prone to kidney stones, consuming high amounts may increase risk as oxalates can bind to calcium and form kidney stones
Those with a history of calcium oxalate kidney stones may be advised to follow a low-oxalate diet restricting oxalates to 40-50 mg per day. Foods high in oxalates provide over 10 mg per serving.
Is Tuna High in Oxalates?
The simple answer is no – tuna is not high in oxalates. Fish and other animal proteins like beef, chicken, pork, eggs and dairy contain no measurable amounts of oxalates. Oxalates are only found in plant sources.
So all types of tuna – including fresh, canned, pouches and frozen – will be oxalate free. You can enjoy tuna without worrying about oxalates contributing to kidney stone risk.
Let’s take a look at the nutrition stats for common tuna preparations:
Canned Tuna (3 oz)
- 0 mg oxalates
- 109 calories
- 0g carbs
- 24g protein
Fresh Tuna Steak (3 oz)
- 0 mg oxalates
- 119 calories
- 0g carbs
- 25g protein
Pouch Tuna (2.5 oz)
- 0 mg oxalates
- 90 calories
- 0g carbs
- 21g protein
As you can see, the oxalate content is 0 mg for a standard serving size of tuna, regardless of type. Plus it provides high quality protein with zero carbs.
Benefits of Tuna for a Low Oxalate Diet
Because tuna is free of oxalates, it can be an excellent addition to a low-oxalate meal plan. Here are some benefits of adding tuna:
- High in protein to replace plant proteins like beans, soy and nuts
- Low in carbs to balance out carb-heavy grains and starchy veggies
- Provides essential omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA
- Good source of potassium, selenium and vitamin B12
- Easy no-cook option with canned and pouches
- Budget-friendly and widely accessible year-round
Tuna is very versatile too. Enjoy it in salads, sandwiches, wraps, poke bowls or tacos for an easy low-oxalate protein source.
Healthy Low Oxalate Meals with Tuna
Here are some recipe ideas that incorporate tuna into low-oxalate meals:
- Tuna salad lettuce wraps with carrot, cucumber, tomato and avocado
- Tuna pasta salad with gluten-free pasta, olives, artichoke hearts and Italian dressing
- Buffalo tuna lettuce cups with hot sauce, blue cheese and celery
- Tuna casserole with cauliflower rice and cheese sauce
- Tuna poke bowl with rice, mango, seaweed salad and avocado
- Mediterranean tuna and chickpea salad with tomatoes, cucumbers, feta and basil
- Tuna melts with tomato, avocado and melted cheese on gluten-free bread
- Tuna tacos on corn tortillas with cabbage slaw and salsa
- Tuna stuffed avocado with lemon and dill
Tuna is endlessly versatile, so get creative with healthy recipes that fit your preferences and restrictions. Avoid high oxalate ingredients like spinach, beans, nuts and wheat flour. Focus on low-oxalate foods like dairy, gluten-free grains, eggs, citrus, carrots, squash and herb seasonings.
Is Drained or Canned Tuna Better?
Canned tuna can be purchased packed in water or oil, and typically contains some extra liquid in the can. For a low oxalate diet, tuna packed in water and drained well is the best option to limit sodium, excess calories and fat.
- Water packed has the lowest fat and calories
- Draining the tuna removes up to 40% of the sodium
- Rinsing tuna further reduces sodium content
Check labels and compare brands, as sodium content can vary widely. Alternatively, fresh tuna will provide the overall healthiest option with more natural flavor.
The Bottom Line
The good news is tuna contains zero measurable oxalates, so it can be included freely on a low oxalate diet. With high protein, omega-3s and no carbs, it makes a smart choice to help balance plant-based oxalate intake.
Focus on water-packed tuna, drain it well and rinse to reduce excess sodium. Then use tuna creatively in salads, bowls, tacos and other recipes while avoiding other high oxalate ingredients. This allows you to safely reap the nutritional benefits of tuna if following a low oxalate meal plan.
Oxalate FAQIs the Kidney Stone Diet just a low oxalate diet?
There is much more to the Kidney Stone Diet® than just lowering oxalate. You can learn more about the Kidney Stone Diet® here, or you can sign up for the Kidney Stone Prevention Course to learn more about all of the diet goals, such as oxalate. What the heck is oxalate?.
Oxalate is a naturally occurring molecule that is found in plants and humans. In plants, oxalate helps get rid of excess calcium. But too much of it in us can cause kidney stones. Oxalate and calcium join together in the kidney and can cause kidney stones. Eighty percent of kidney stones are calcium oxalate.
This is the gold standard oxalate list researched and published by the folks at Harvard. People all the time ask me, “Why should I trust this list when there are so many others?” I’ve always given them the same answer: We (Dr. Many doctors, including Coe and me, trust this list because it helps our patients lower the amount of oxalate in their urine. We know it works.
Did you try keto, low carb, or are you a vegan or vegetarian? Did you eat healthy (lots of almonds and spinach) and lose weight but gain a stone? I’ve heard all of these things and more. Point is, I can help. Should I be avoiding oxalates?.
Some people think that you should stay away from all oxalates. This is not only wrong and bad for you, but it’s also impossible because our bodies make oxalate—some of us more than others. Oxalate is a by-product of general metabolism. Get your reliable Harvard Oxalate Food List here. What do oxalates do to the body?.
Oxalate joins with calcium in our kidneys and can form stones. The more oxalate we eat and make, the more likely it is that these two salts will mix. This is especially true if we don’t drink enough water and pee out the extra. Learn more about oxalate here. What foods have high oxalates?.
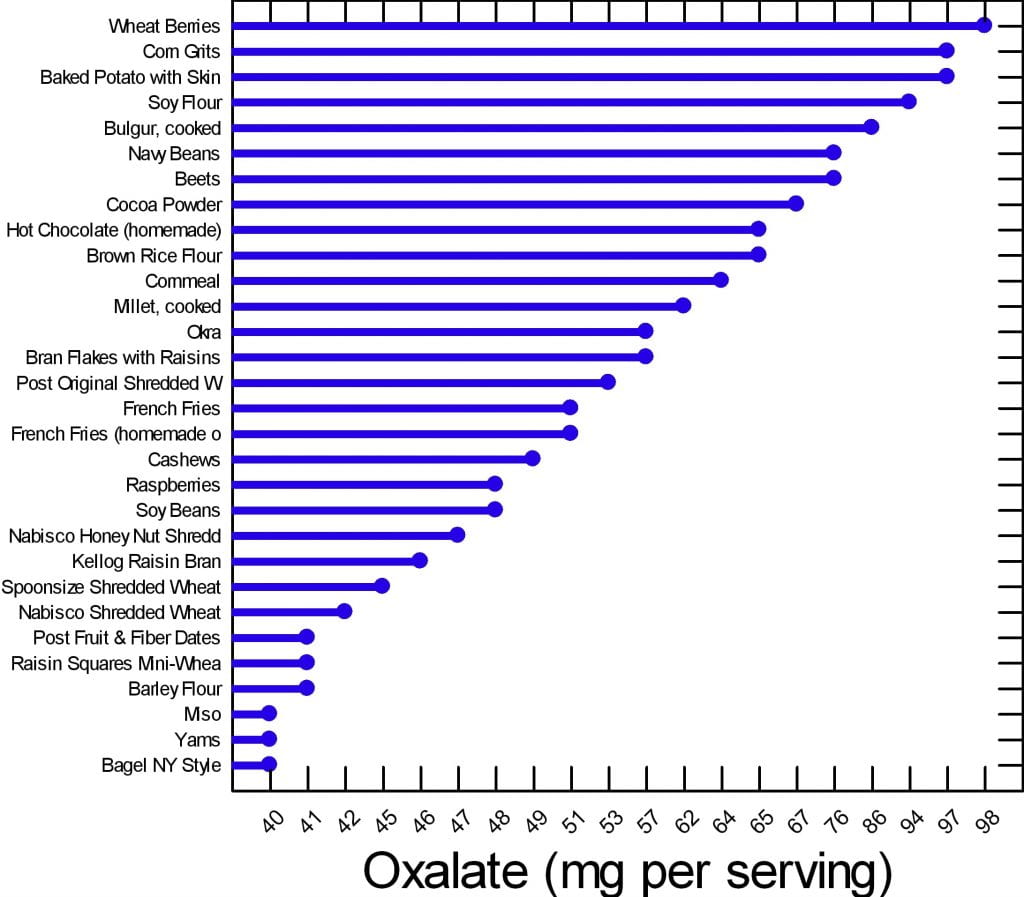
Find the foods that have the most oxalate here: Spinach, Rhubarb, Rice Bran, Buckwheat Groats, Almonds, Miso Soup, Wheat Berries, Corn Grits, Baked Potato with Skin, and Soy Beans. This list is in order of the foods that have the most oxalate. Get your Harvard oxalate list here. How do you flush oxalates out of your body?.
Start by giving up spinach and almond products (like almond milk and flour—I see you keto folks). These are the foods that people eat too much of the most. Then you need to make sure you get enough calcium every day. Getting enough calcium will keep your body from reabsorbing oxalate. What are the symptoms of high oxalates?.
First and foremost kidney stones. What are the worst foods for oxalates?
Harvard looked at ten foods and found that they had the most oxalate. They are (in order of highest oxalate content): Soy beans, Spinach, Rhubarb, Rice Bran, Buckwheat Groats, Almonds, Miso Soup, Wheat Berries, Corn Grits, Baked Potato with Skin, and Wheat Berries. Get your Harvard oxalate list here.
The most overeaten foods are almonds (and almond milk and almond flour), cashews, and spinach. Chocolate, beets, teas, beans, peanut butter, and sweet potatoes are some other high-oxalate foods that people often eat or drink too much of. This doesn’t mean you must give up all these foods and drinks. It does mean you should cut back on these common high-oxalate foods and make sure you get enough calcium every day. Go here for your Harvard oxalate food list. Is coffee high in oxalates?.
Coffee is not high in oxalate. But drinking too much (over a few cups per day) can lead to dehydration. So, make sure you are getting your water goals met. Get your Harvard oxalate list here. Does drinking lots of water flush out oxalates?.
Eating less oxalate will lower oxalates. Fluids are very important for you as they will decrease the urine saturation and keep you well-hydrated. When you are well hydrated, you will have fewer stone-forming salts lingering around. Get your reliable oxalate food list by Harvard here. Are eggs high in oxalates?.
Eggs have no oxalates. Here is a list of high-oxalate foods. Get your reliable oxalate food list by Harvard here. Are bananas high in oxalates?.
Bananas as studied by Harvard is 10. 3mg of ox per 1 banana. You can find Harvard’s oxalate food list here. Does lemon water help oxalates?.
No, lemon juice can help a little by making your urine more alkaline. This may help people whose urine is too acidic. Not everyone should be using lemons as a kidney stone prevention tactic. You can find out if a lemon might help you avoid getting new kidney stones by collecting urine for 24 hours. Get your reliable oxalate food list by Harvard here. What does oxalate in urine look like?.
There have been no human studies that prove magnesium will remove excess oxalate. Find your reliable oxalate food list here. What neutralizes oxalates?.
Your body’s oxalate level can be lowered by avoiding foods that are high in oxalate and making sure you get enough calcium every day from foods and drinks. Here is more information on getting your calcium needs met. Are blueberries high in oxalates?.
Blueberries are medium in oxalate. Harvard studied them as being 18. 5 mg per 1/2 cup of blueberries. Find your reliable oxalate food list here. Is avocado high in oxalates?.
Avocados can safely be eaten on a lower oxalate diet. Harvard studied them as being 19 mg/oxalate per 1 whole med avocado. Find your reliable oxalate food list here. Is peanut butter full of oxalates?.
Peanut butter can safely be eaten on a low oxalate diet if eaten within portion size. Harvard studied peanut butter as being 38. 4 mg/oxalate per 2 tablespoons of peanut butter. Find your oxalate food list here. What drinks are high in oxalate?.
Black tea and iced teas made with black tea can be higher in oxalate. Stick with 1 – 2 cups per day and don’t overly steep. The more you steep, the higher the oxalate. Find your oxalate food list here. Is oatmeal high in oxalate?.
Harvard has studied oatmeal and it comes in as zero oxalate per cup. Find your oxalate food list here. What are the 10 foods that cause kidney stones?.
Harvard looked at ten foods and found that they had the most oxalate. They are (in order of highest oxalate content): Soy beans, Spinach, Rhubarb, Rice Bran, Buckwheat Groats, Almonds, Miso Soup, Wheat Berries, Corn Grits, Baked Potato with Skin, and Wheat Berries. Get your Harvard oxalate list here. Do epsom salt baths help oxalates?.
Epsom salts will not remove oxalates. Get your Harvard oxalate list here. Is green tea high in oxalates?
There are been numerous studies on green tea and it comes in as low on the oxalate scale. Get your Harvard oxalate list here. What is the fastest way to flush your kidneys?.
There is not such thing as a potion or pill to “flush” your kidneys. Drink fluids and that will help keep your urine saturations low. You want to stay well hydrated to prevent kidney stones. Is there a home test for oxalates?.
There is no reliable home test for oxalates. Get your reliable oxalate food list by Harvard here. What supplements bind oxalates?.
There are no supplements that have been proven to bind oxalates in humans. Get your reliable oxalate food list by Harvard here. Do oxalates damage kidneys?.
Primary hyperoxaluria which is a rare disease can cause damage to your kidneys. Get your reliable oxalate food list by Harvard here. How do I know if I need to avoid oxalates?.
If you’ve had kidney stones before, you should ask your doctor to record your urine for 24 hours to find out if oxalate is what’s causing them again. There are several reasons why people form kidney stones, oxalate is just one of them. Get your reliable oxalate food list by Harvard here. Should I worry about oxalates?.
If you have had kidney stones before, you should be careful about eating and drinking too many things that are high in oxalate. Get your reliable oxalate food list by Harvard here.

Type in your email address to get both of my Simple
OXALATES (7 High Oxalate Foods) Sensitive to Oxalates?
FAQ
Does tuna fish have oxalates in it?
Is canned tuna okay for kidney stones?
What are the worst foods for oxalates?
Are fish high in oxalates?
What foods are low oxalate?
Choosing low-oxalate proteins like poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products like cheese or yogurt, legumes such as lentils and chickpeas and nuts or seeds such as peanuts and sunflower seeds can provide good sources for nutrients while also reducing the risk of consuming too many oxalates. III. Problems Caused by High-Oxalate Levels
What foods are high in oxalates?
Some of the foods rich in oxalates are beets, nuts, spinach, wheat germ, cocoa powder, chard, figs, and aubergines, among others.
Are nuts high in oxalates?
Nuts in any form are considered to be high in oxalates. This means nut butter and pastes are also included on this list. A single 100-gram serving of tree nuts contains about 200 mg of oxalates. That’s almost five times more than the recommended daily amount of 40 mg! 4. Seeds
Are canned foods high in oxalates?
Processed and canned foods are chock full of oxalates, too. Canned goods aren’t just high in oxalates, but they’re also loaded with sodium and phosphorus—two substances that don’t do any good for your body.
