Poultry farming aims to raise chickens, ducks, turkeys, and other birds for their meat, which provides a steady and cheap source of protein for people to eat.
Egg Production: Another key objective is to produce eggs for consumption. A big part of the world’s egg supply comes from chicken farms, which meet the high demand for this healthy food.
Economic Livelihood: Poultry farming is a way for many people and families to make a living, giving them jobs and money in both rural and urban areas.
Food Security: Chicken farming helps with food security by providing a variety of protein sources and lowering the reliance on traditional livestock. This makes it easier to meet the nutritional needs of a growing population.
Nutritional Value: Poultry products are full of important nutrients like protein, vitamins (B-complex vitamins), and minerals (iron, zinc). They can help you eat a healthy, balanced diet.
Quick Turnaround: The production cycle for chickens is shorter than that of many other animals. This means that the business can turn over its products faster, make more money, and use its resources more efficiently.
Sustainable Agriculture: Poultry farming can be a part of sustainable agriculture by using organic waste as feed, keeping pests away, and making the soil more fertile by adding manure.
Use of Byproducts: Feathers and offal, which are byproducts of chicken farming, can be used to make valuable things like feather meals for animal feed or pet food, as well as as raw materials for many other industries.
Genetics, disease resistance, and vaccine development are some of the areas where raising chickens helps biomedical research. This is because birds and humans share many genetic similarities.
Rural Development: Poultry farming can help rural economies by creating jobs and income, which can help keep people from moving to cities.
Adaptability: Poultry can be raised in a wide range of climates and environments, which makes it easy to get and use in many places.
Exports and Trade: Poultry products can make a big difference in how much money a country makes from exports, which helps the economy through trade.
Skills Development: Poultry farming offers a platform for skill development in animal husbandry, veterinary care, management, and entrepreneurship.
Education and Awareness: Poultry farming can be used to teach people about taking care of animals, making food, and eating responsibly.
Disease Control: Keeping biosecurity measures in place, raising chickens helps stop the spread of diseases in the livestock industry and the chance that they will reach people.
Protecting and enhancing the genetic diversity of poultry breeds can be helped by raising chickens. Heritage breeds can be kept alive and changed to fit modern needs.
Technology and Innovation: Raising chickens promotes the creation and use of new technologies, like climate control, automated feeding systems, and management based on data.
Social Engagement: Raising chickens can get farmers involved in their communities and help them work together, which can lead to sharing information and building support networks.
Effects on the Environment: Using sustainable farming methods can lower the damage done to the environment by making better use of resources and managing waste.
Public Health: Poultry farming is good for public health because it produces safe and healthy food, encourages good hygiene, and helps keep an eye on zoonotic diseases.
To sum up, raising chickens is an important part of modern agriculture because it helps with food production, economic growth, environmental protection, and public health.
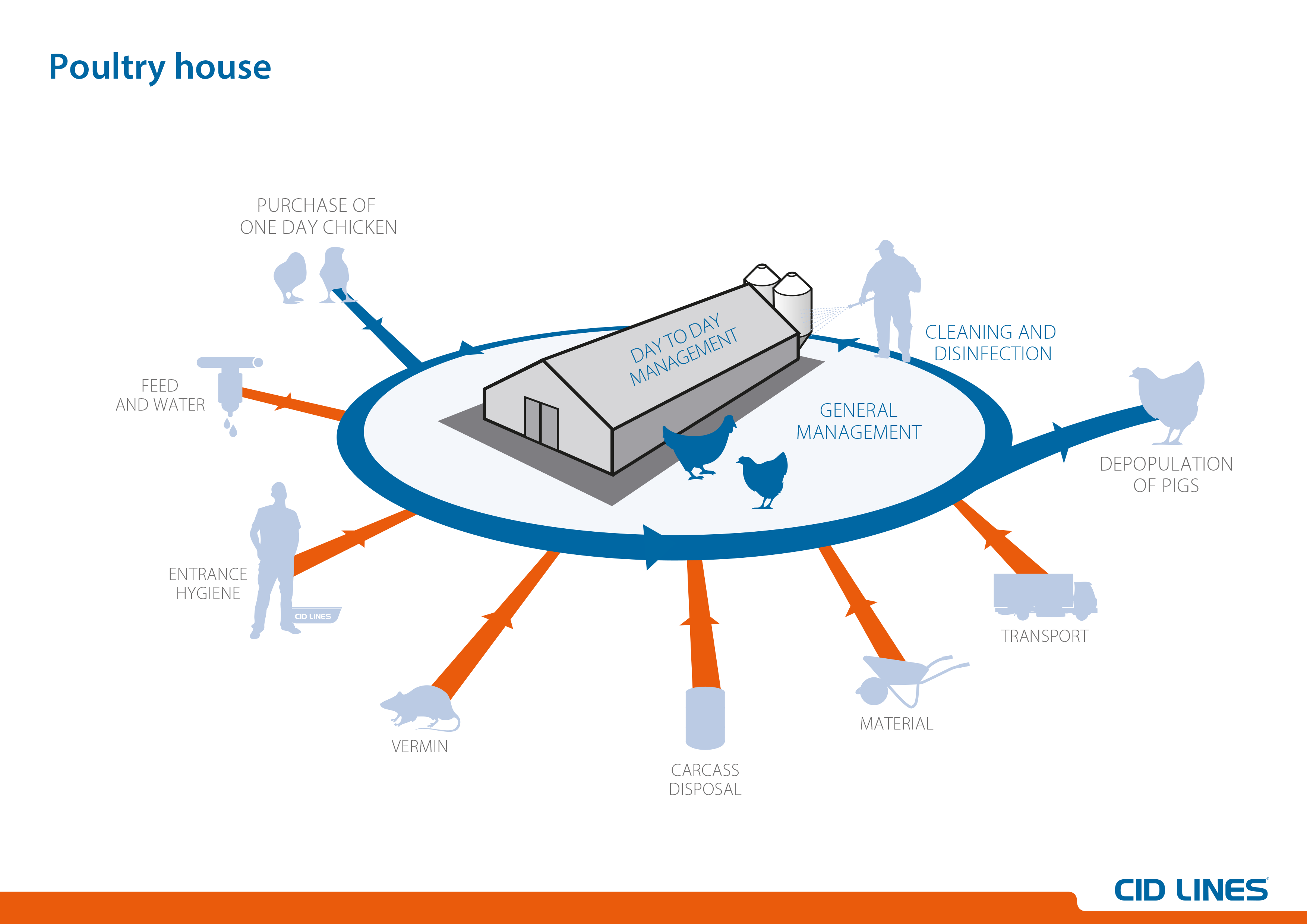
Poultry farming involves raising domesticated birds like chickens turkeys ducks, and geese for meat, eggs, feathers, or manure production. As with any agricultural practice, poultry farmers work to meet certain core objectives. Knowing the main goals driving the poultry industry provides insight into this vital sector of agriculture.
The overarching aim of operating a poultry farm is to sustainably raise birds and optimize output of poultry products. But fulfilling that broad goal requires targeting some specific objectives. Here are the primary objectives behind poultry farming:
Producing Poultry Meat
One of the main objectives of poultry farms is to raise birds for meat production. Chickens, ducks, turkeys and other fowl provide an efficient source of animal protein that is prized worldwide. Poultry meat delivers essential amino acids, iron, zinc, phosphorus and other key nutrients. By methodically producing birds to harvest for meat, poultry farming helps satisfy global dietary needs.
The aim is to raise flocks using practices and genetics that maximize meat yield per bird. Feed rations and housing conditions are optimized so birds grow rapidly while staying healthy. Processing birds at the ideal age and weight results in the desired quantity and quality of lean poultry meat for consumers.
Generating Eggs for Food
Along with meat production, egg farming is another major focus of poultry operations Hens bred for egg laying can produce up to 300 eggs annually. Turkey and other fowl also lay eggs that serve as an affordable protein source.
To achieve efficient egg production, birds are given balanced feed promoting ovarian development and egg formation Proper lighting schedules trigger hormones that optimize laying rates The goal is to maximize the number and size of eggs from each hen during peak production years.
Feather and Down Harvesting
While lesser known, feather and down harvesting is a common objective on some poultry farms. Mature ducks and geese grown specifically for their plumage are plucked multiple times per year. The down and feathers are used as insulating, soft filling in coats, bedding and other goods.
The aim is to produce quality feathers and down in certain desired colors, lengths or textures. Breed selection, nutrition and other management practices optimize plumage yield and traits to meet market demand. This creates an added income stream for producers.
Fertilizer Production
Poultry farms accumulate a significant amount of manure from all those birds. While this manure must be properly handled, it also presents an opportunity as a rich organic fertilizer. Spreading aged poultry litter on fields provides nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and other nutrients that nourish soils and crops.
By composting manure for fertilizer use, poultry farms can offset costs and generate income through manure sales. As an integrated objective, manure output can enhance sustainability and supplement revenue. Proper manure management also minimizes environmental impacts.
Genetic Improvement
Specialized poultry breeding operations aim to improve genetics through selective breeding. By carefully choosing and mating superior birds over generations, populations are developed with advantageous traits. This quality breeding stock then propagates those genetics throughout commercial flocks.
Desired traits may include rapid growth, high egg production, disease resistance, feed efficiency, carcass yield and more. Breeding programs allow poultry producers to continuously enhance performance and output over time through genetic gain.
Supporting Integrated Farming Systems
Some poultry farms aim to complement other agricultural enterprises in an integrated system. For instance, poultry manure from mobile chicken coops can fertilize crops or pasture. Rotating poultry through fields aids weed and pest control.
In aquaculture systems, poultry litter provides nutrients to fertilize plankton. The integrated system seeks to maximize resource use and sustainability through symbiotic practices.
Providing Livelihoods and Economic Opportunity
On a broader level, an overarching objective of poultry farming is to support producers and communities economically through income, local jobs and food production. Poultry offers dependable income and nourishment. For rural areas and developing regions, poultry can sustain families and neighborhoods.
Whether supplying eggs for income or meat for food, poultry farming aims to positively contribute to people’s livelihoods. The full benefits are best achieved when environmental and humane standards are also upheld.
Achieving Sustainable Production
Ultimately, all the objectives of a poultry farm must align with long-term sustainability. Responsible practices ensure poultry production meets current needs while maintaining productivity and resources over time.
By pursuing goals like resource efficiency, animal welfare, ecology, fair labor and food safety along with production output, the poultry industry can keep providing for tomorrow while feeding the world today.
About Sb group nepal
Saresh Babita Group (SBG) is a consolidated firm of diverse enterprises. It was founded in 2018 to affiliate and deliver its products with one business name. It was first started in 1995 by Mr. Saresh Kumar Saraff, ventured into sugar manufacturing and distribution in Nepal. After this one success, a lot of different kinds of businesses sprung up and quickly became market leaders in Nepal. Today SBG leads six diverse business sectors with one passion: delivering the best of all products.
Objectives of Poultry housing | World of Poultry
FAQ
Why are poultry farms important?
What are the objectives of poultry manure?
What are the objectives of brooding in poultry?
What are the benefits of poultry?
